![]()
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Table of Contents
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar – Hello friends, in today’s article, we will explore in Hindi what pronouns are, their definition, and the various types of pronouns. Pronouns play a crucial role in grammar as a significant part of speech. Understanding pronouns not only improves our sentence structure but also enhances communication. So, let’s dive into this article and understand pronouns in Hindi step by step.
Pronoun definition in Hindi
Definition of Pronoun: Words that are used in place of a noun to stop its repetition are called pronouns.
By using pronouns, we can make any sentence much easier to read and understand.
For example, if we do not use pronouns, sentences would look something like this:
- Rohan is a smart boy. (रोहन एक चालाक लड़का है।)
- Rohan lives in Delhi. (रोहन दिल्ली में रहता है।)
- Rohan has a car. (रोहन के पास कार है।)
Using the same Pronoun the sentences would look something like this:
- Rohan is a clever boy. (महेश एक चालाक लड़का है।)
- He lives in Patna. (वह पटना में रहता है।)
- He has a bike. (उसके पास बाइक है।)
As you saw in the above sentences, instead of Rohan, we used He. Due to which the sentence seems easy to read and listen.
Similarly, we can make the sentences short and easy by using pronouns.
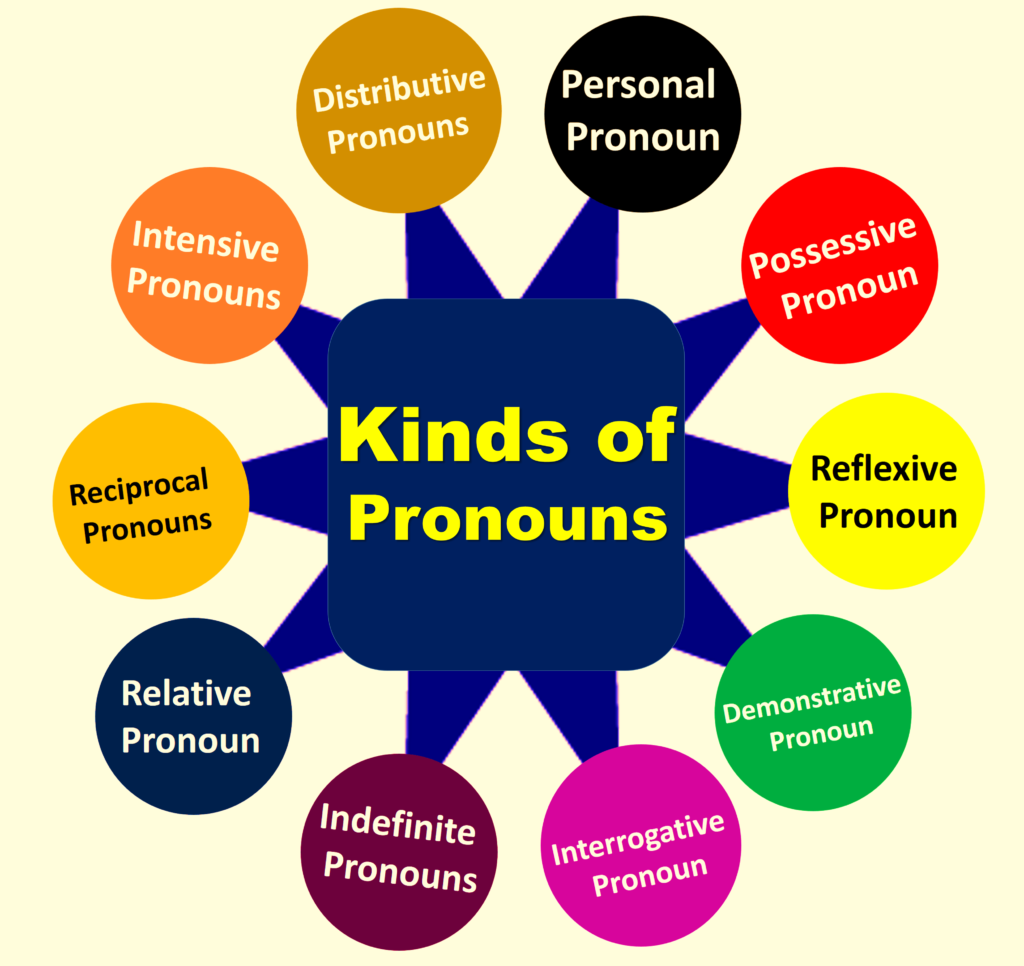
Types/Kinds of Pronoun
सर्वनाम (Pronoun) मुख्यतः 10 प्रकार के होते है:
- Personal Pronoun (पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Reflexive Pronoun (निजवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Emphatic / Intensive pronoun (बलात्मक सर्वनाम)
- Demonstrative Pronoun (संकेतवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Indefinite Pronoun (अनिश्चितवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Distributive Pronoun (विभागवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Relative Pronoun (संबंधवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Interrogative Pronoun (प्रश्नवाचक सर्वनाम)
- Reciprocal Pronoun (पारस्परिक सर्वनाम)
- Possessive Pronoun (अधिकारवाचक सर्वनाम)
Personal Pronoun: Definition and Examples
Definition:
A personal pronoun is a pronoun used to refer to a specific person or thing. Personal pronouns change based on number (singular or plural), person (first, second, or third), gender (male, female, or neutral), and case (subject, object, or possessive).
Personal pronouns are divided into three categories based on person:
1. First Person: Refers to the person speaking (I, we, me, us).
(पहला व्यक्ति: बोलने वाले व्यक्ति के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।)
2. Second Person: Refers to the person being spoken to (you).
(दूसरा व्यक्ति: जिस व्यक्ति से बात की जा रही है उसके लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।)
3. Third Person: Refers to the person or thing being spoken about (he, she, it, they, him, her, them).
(तीसरा व्यक्ति: जिस व्यक्ति या वस्तु के बारे में बात की जा रही है उसके लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।)
Examples with Hindi Translations
1. First Person Pronouns:
I: I am going to the market.
(मैं बाजार जा रहा हूँ।)
We: We are friends.
(हम दोस्त हैं।)
Me: He gave me a book.
(उसने मुझे एक किताब दी।)
Us: They invited us to the party.
(उन्होंने हमें पार्टी में आमंत्रित किया।)
2. Second Person Pronouns:
You: You are a good singer.
(तुम एक अच्छे गायक हो।)
You (Plural): You all need to be quiet.
(आप सभी को चुप रहना चाहिए।)
3. Third Person Pronouns:
He: He is my brother.
(वह मेरा भाई है।)
She: She is a doctor.
(वह एक डॉक्टर है।)
It: It is raining outside.
(बाहर बारिश हो रही है।)
They: They are playing football.
(वे फुटबॉल खेल रहे हैं।)
Him: I gave him the keys.
(मैंने उसे चाबी दी।)
Her: He called her yesterday.
(उसने उसे कल बुलाया था।)
Them: We saw them at the mall.
(हमने उन्हें मॉल में देखा।)
Cases of Personal Pronouns
1. Subjective Case (When the pronoun acts as the subject):
– I, we, you, he, she, it, they
– Example: She is reading a book.
(वह एक किताब पढ़ रही है।)
2. Objective Case (When the pronoun acts as the object):
– me, us, you, him, her, it, them
– Example: They gave us a gift.
(उन्होंने हमें एक तोहफा दिया।)
3. Possessive Case (Shows ownership or possession):
– my/mine, our/ours, your/yours, his, her/hers, its, their/theirs
– Example: This is my book.
(यह मेरी किताब है।)
– Example: The house is theirs.
(यह घर उनका है।)
Detailed Notes with Hindi Translation
Personal pronouns help make sentences clearer and avoid the repetition of nouns. For example, without personal pronouns, we would have to repeat nouns constantly, making sentences sound awkward and confusing.
Example without personal pronouns:
Ravi went to Ravi’s school because Ravi forgot Ravi’s bag.
(रवि रवि के स्कूल गया क्योंकि रवि अपना बैग भूल गया था।)
Example with personal pronouns:
He went to his school because he forgot his bag.
(वह अपने स्कूल गया क्योंकि वह अपना बैग भूल गया था।)
By using personal pronouns, we make communication smoother and more natural. Personal pronouns are essential to simplify sentences and make communication clearer.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Reflexive Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition:
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers back to the subject of the sentence. It is used when the subject and the object of the verb are the same person or thing.
वह सर्वनाम जिसमें कर्ता (subject) द्वारा किया गया कार्य किसी दूसरे पर न पढ़कर खुद पर पढ़ता है। उसे निजवाचक सर्वनाम (reflexive pronoun) कहते है।
Reflexive pronouns end in “-self” for singular (e.g., myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself) and “-selves” for plural (e.g., ourselves, yourselves, themselves).
Reflexive pronoun meaning in Hindi
Reflexive pronoun का हिंदी अर्थ होता है- “निजवाचक सर्वनाम“।
Reflexive Pronouns in English:
- Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
- Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
In Hindi, reflexive pronouns are typically translated as forms of “स्वयं” or “खुद.”
Examples with Hindi Translations
1. Myself
I hurt myself while cooking.
(मैंने खाना बनाते समय खुद को चोट पहुंचाई।)
I introduced myself to the new neighbors.
(मैंने अपने नए पड़ोसियों से खुद का परिचय कराया।)
2. Yourself
You should take care of yourself.
(तुम्हें अपना ध्यान रखना चाहिए।)
Did you finish the project yourself?
(क्या आपने खुद प्रोजेक्ट पूरा किया?)
3. Himself
He blamed himself for the mistake.
(उसने गलती के लिए खुद को दोषी ठहराया।)
He prepared the meal by himself.
(उसने खुद से खाना बनाया।)
4. Herself
She taught herself to play the guitar.
(उसने खुद गिटार बजाना सीखा।)
She looked at herself in the mirror.
(वह आईने में खुद को देख रही थी।)
5. Itself
The cat groomed itself.
(बिल्ली ने खुद को साफ किया।)
The company prides itself on quality.
(कंपनी खुद को गुणवत्ता पर गर्व करती है।)
6. Ourselves
We enjoyed ourselves at the party.
(हमने पार्टी में खुद का खूब आनंद लिया।)
We should challenge ourselves to do better.
(हमें खुद को बेहतर करने के लिए चुनौती देनी चाहिए।)
7. Yourselves (plural)
You all should help yourselves to some food.
(आप सभी को खुद से कुछ खाना लेना चाहिए।)
Did you do the work yourselves?
(क्या आपने खुद काम किया?)
8. Themselves
They blamed themselves for the loss.
(उन्होंने नुकसान के लिए खुद को दोषी ठहराया।)
The kids enjoyed themselves at the park.
(बच्चों ने पार्क में खूब मज़े किए।)
When to Use Reflexive Pronouns
1. When the subject and the object are the same:
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject of the sentence does something to themselves.
He cut himself while shaving.
(उसने शेव करते समय खुद को काट लिया।)
2. For emphasis:
Reflexive pronouns can also be used to emphasize that someone did something without help.
She herself designed the entire project.
(उसने खुद पूरे प्रोजेक्ट को डिजाइन किया।)
We did it ourselves.
(हमने इसे खुद किया।)
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
In reflexive pronouns, the action returns to the subject. For instance, in the sentence “I hurt myself,” the subject “I” and the object “myself” refer to the same person.
Example without reflexive pronouns:
I hurt me.
(मैंने मुझे चोट पहुंचाई।) — Incorrect, because “me” does not reflect back to “I.”
Example with reflexive pronouns:
I hurt myself.
(मैंने खुद को चोट पहुंचाई।) — Correct, because “myself” reflects back to the subject “I.”
Reflexive pronouns are used not just for clarity, but also for emphasizing actions done by oneself. They make sentences more natural and grammatically correct.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Emphatic Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition: An emphatic pronoun is a pronoun that is used to emphasize a noun or another pronoun. It is the same form as a reflexive pronoun (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), but its function is different. While reflexive pronouns reflect the action back to the subject, emphatic pronouns add emphasis to the subject performing the action.
Emphatic Pronouns in English:
- Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
- Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
In Hindi, emphatic pronouns are often translated as “स्वयं” or “खुद” to add emphasis.
Examples with Hindi Translations
1. Myself
I myself completed the project.
(मैंने स्वयं यह प्रोजेक्ट पूरा किया।)
I myself will talk to him.
(मैं खुद उससे बात करूंगा।)
2. Yourself
You yourself told me this.
(तुमने खुद मुझे यह बताया था।)
You yourself should go there.
(तुम्हें खुद वहां जाना चाहिए।)
3. Himself
He himself made the decision.
(उसने खुद यह निर्णय लिया।)
The CEO himself welcomed the guests.
(सीईओ ने स्वयं मेहमानों का स्वागत किया।)
4. Herself
She herself solved the problem.
(उसने स्वयं समस्या को हल किया।)
She herself baked the cake.
(उसने खुद केक बनाया।)
5. Itself
The machine itself is very efficient.
(मशीन खुद ही बहुत प्रभावी है।)
The dog itself opened the door.
(कुत्ते ने खुद दरवाजा खोला।)
6. Ourselves
We ourselves need to fix this.
(हमें खुद इसे ठीक करने की आवश्यकता है।)
We ourselves organized the event.
(हमने स्वयं इस कार्यक्रम का आयोजन किया।)
7. Yourselves (plural)
You yourselves must take responsibility.
(आपको खुद ही जिम्मेदारी लेनी चाहिए।)
You yourselves need to complete the task.
(आपको स्वयं कार्य पूरा करना चाहिए।)
8. Themselves
They themselves admitted their mistake.
(उन्होंने खुद अपनी गलती मानी।)
The children themselves cleaned the room.
(बच्चों ने खुद कमरे की सफाई की।)
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
Emphatic pronouns are used to highlight or stress the importance of the subject in performing the action. These pronouns do not change the meaning of the sentence but add emphasis to the fact that the subject carried out the action without help or to show the importance of the subject.
Example without emphatic pronoun:
I completed the project.
(मैंने प्रोजेक्ट पूरा किया।)
Example with emphatic pronoun:
I myself completed the project.
(मैंने स्वयं यह प्रोजेक्ट पूरा किया।)
In this example, the addition of “myself” emphasizes that I, and no one else, completed the project.
Difference Between Reflexive and Emphatic Pronouns
Although emphatic and reflexive pronouns look the same, their usage differs:
1. Reflexive pronouns reflect the action back to the subject.
Example: He hurt himself.
(उसने खुद को चोट पहुंचाई।)
2. Emphatic pronouns add emphasis to the subject without changing the meaning.
Example: He himself did the work.
(उसने स्वयं काम किया।)
Common Uses of Emphatic Pronouns
1. To emphasize the subject: When the speaker wants to stress that the subject did something by themselves.
She herself designed the house.
(उसने खुद घर डिजाइन किया।)
2. To clarify who performed the action: Emphatic pronouns clarify that a specific person was responsible for the action.
The teacher herself checked the papers.
(शिक्षक ने खुद पेपर्स चेक किए।)
Emphatic pronouns are valuable in conversation and writing to highlight the subject’s importance or to stress that no one else was involved in the action. They add clarity and emphasis to the sentence, making the statement more impactful.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Demonstrative Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition:
A demonstrative pronoun is used to point to and identify a specific noun or nouns. Demonstrative pronouns refer to something near or far in distance or time. In English, the demonstrative pronouns are this, that, these, and those.
- This and these refer to things that are near.
- That and those refer to things that are far.
In Hindi, demonstrative pronouns are often translated as “यह,” “वह,” “ये,” and “वे,” depending on proximity and number.
Demonstrative Pronouns in English
- Singular: this, that
- This refers to something close in distance or time.
- That refers to something far in distance or time.
- Plural: these, those
- These refers to things that are close in distance or time.
- Those refers to things that are far in distance or time.
Examples with Hindi Translations
- This (यह)
- This is my book.
(यह मेरी किताब है।) - This is delicious.
(यह स्वादिष्ट है।)
- This is my book.
- That (वह)
- That is his house.
(वह उसका घर है।) - That was a great movie.
(वह बहुत अच्छी फिल्म थी।)
- That is his house.
- These (ये)
- These are my keys.
(ये मेरी चाबियां हैं।) - These are fresh fruits.
(ये ताजे फल हैं।)
- These are my keys.
- Those (वे)
- Those are her shoes.
(वे उसके जूते हैं।) - Those were the good old days.
(वह अच्छे पुराने दिन थे।)
- Those are her shoes.
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
Demonstrative pronouns are used to indicate specific people or things, either near or far from the speaker. The key difference between the pronouns lies in whether the noun being referred to is singular or plural, and whether it is close or far in relation to the speaker.
Use of ‘This’ and ‘These’
1. This (singular) is used to refer to something near to the speaker.
-
- This is my phone.
(यह मेरा फोन है।)
- This is my phone.
Here, “this” points to a phone that is near the speaker.
2. These (plural) is used to refer to multiple things that are near the speaker.
-
- These are my books.
(ये मेरी किताबें हैं।)
- These are my books.
“These” refers to several books close to the speaker.
Use of ‘That’ and ‘Those’
1. That (singular) is used to refer to something far from the speaker.
-
- That is the tallest building.
(वह सबसे ऊंची इमारत है।)
- That is the tallest building.
“That” points to a distant building.
2. Those (plural) is used to refer to multiple things that are far from the speaker.
-
- Those are my friends.
(वे मेरे दोस्त हैं।)
- Those are my friends.
“Those” indicates friends who are not near the speaker.
Demonstrative Pronouns in Time Context
Demonstrative pronouns can also refer to time, not just physical distance.
1. This can refer to the present or something current.
-
- This is a difficult time.
(यह कठिन समय है।)
- This is a difficult time.
This refers to the present situation.
2. That can refer to something in the past or future.
-
- That was a great day.
(वह बहुत अच्छा दिन था।)
- That was a great day.
Here, “that” refers to a day in the past.
1. These can refer to recent times or multiple current events.
-
- These are hard times.
(ये कठिन समय हैं।)
- These are hard times.
“These” points to the current difficult times.
2. Those can refer to events or times in the past or distant future.
-
- Those were the days.
(वह अच्छे दिन थे।)
- Those were the days.
“Those” refers to past, memorable days.
Difference Between Demonstrative Pronouns and Demonstrative Adjectives
It’s important to note that demonstrative pronouns stand alone, while demonstrative adjectives modify a noun.
- Demonstrative Pronoun: This is my bag.
(यह मेरा बैग है।)
“This” stands on its own.
- Demonstrative Adjective: This bag is mine.
(यह बैग मेरा है।)- “This” describes the noun “bag.”
Key Points to Remember
- This/These = Things that are near.
- That/Those = Things that are far.
Demonstrative pronouns can refer to physical distance or time.
Example Summary:
- This is singular and near.
(यह पास में है।) - That is singular and far.
(वह दूर है।) - These is plural and near.
(ये पास में हैं।) - Those is plural and far.
(वे दूर हैं।)
These pronouns help identify and specify particular items or times, making communication clearer and more precise.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Indefinite Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition:
An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that refers to a non-specific person, place, thing, or quantity. Unlike personal pronouns, which refer to specific individuals, indefinite pronouns are used when we don’t know exactly who or what we’re referring to. Common indefinite pronouns include someone, something, anyone, anything, everyone, everything, nobody, none, few, many, several, all, and some.
In Hindi, indefinite pronouns are translated depending on the context, such as “कोई,” “कुछ,” “सब,” “किसी,” “कुछ लोग,” etc.
Types of Indefinite Pronouns
- Singular Indefinite Pronouns: Refer to one person or thing (e.g., someone, something, anyone, anything, nobody, each).
- Plural Indefinite Pronouns: Refer to more than one person or thing (e.g., many, few, several).
- Pronouns that can be Singular or Plural: Depending on the context (e.g., all, none, some).
Examples with Hindi Translations
- Someone (कोई व्यक्ति)
- Someone is at the door.
(कोई दरवाजे पर है।) - Someone left their bag here.
(किसी ने अपना बैग यहां छोड़ा है।)
- Someone is at the door.
- Something (कुछ)
- Something is missing from the shelf.
(शेल्फ से कुछ गायब है।) - I need something to eat.
(मुझे कुछ खाने के लिए चाहिए।)
- Something is missing from the shelf.
- Anyone (कोई भी)
- Is anyone home?
(क्या घर में कोई है?) - Anyone can do this job.
(यह काम कोई भी कर सकता है।)
- Is anyone home?
- Anything (कुछ भी)
- I don’t want anything.
(मुझे कुछ भी नहीं चाहिए।) - Do you need anything?
(क्या तुम्हें कुछ चाहिए?)
- I don’t want anything.
- Everyone (हर कोई)
- Everyone is invited to the party.
(हर किसी को पार्टी में बुलाया गया है।) - Everyone has their own opinion.
(हर किसी की अपनी राय होती है।)
- Everyone is invited to the party.
- Nobody (कोई नहीं)
- Nobody knows the answer.
(कोई जवाब नहीं जानता।) - Nobody was there at the time.
(उस समय वहां कोई नहीं था।)
- Nobody knows the answer.
- None (कोई नहीं)
- None of the students passed the test.
(छात्रों में से कोई भी परीक्षा में पास नहीं हुआ।) - None of this makes sense.
(इसमें से कुछ भी समझ में नहीं आता है।)
- None of the students passed the test.
- Few (कुछ लोग)
- Few understand the importance of this.
(कुछ लोग इसके महत्व को समझते हैं।) - Few were chosen for the competition.
(कुछ को प्रतियोगिता के लिए चुना गया था।)
- Few understand the importance of this.
- Many (बहुत से)
- Many people attended the event.
(बहुत से लोग इस कार्यक्रम में आए थे।) - Many of them are my friends.
(उनमें से कई मेरे दोस्त हैं।)
- Many people attended the event.
- All (सब)
- All are welcome to join the meeting.
(सभी का बैठक में स्वागत है।) - All of the cookies are gone.
(सारे बिस्किट खत्म हो गए हैं।)
- All are welcome to join the meeting.
- Some (कुछ)
- Some of the students were late.
(कुछ छात्र देर से आए थे।) - Would you like some tea?
(क्या आप कुछ चाय लेंगे?)
- Some of the students were late.
- Several (कई)
- Several people came to help.
(कई लोग मदद के लिए आए थे।) - Several students failed the exam.
(कई छात्र परीक्षा में फेल हो गए।)
- Several people came to help.
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
Singular Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns like someone, something, anyone, anything, nobody, and each refer to singular entities, even though the specific identity is unknown.
- Someone refers to an unknown person.
Example: Someone has stolen my pen.
(किसी ने मेरा पेन चुरा लिया है।) - Something refers to an unknown object.
Example: Something smells good in the kitchen.
(रसोई में कुछ अच्छा महक रहा है।) - Anyone refers to any person, without specifying who.
Example: Can anyone help me with this?
(क्या कोई मेरी इसमें मदद कर सकता है?)
Plural Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns like many, few, several are plural and refer to more than one person or thing.
- Few refers to a small number of people or things.
Example: Few understood the lesson.
(कुछ लोग ही सबक को समझ पाए।) - Several means more than two but not many.
Example: Several students were absent today.
(कई छात्र आज अनुपस्थित थे।)
Pronouns That Can Be Singular or Plural
Indefinite pronouns like all, none, some can be both singular or plural depending on the context.
- All can refer to everything or everyone.
Example: All of the cake is gone.
(सारा केक खत्म हो गया है।)- This sentence refers to a singular cake.
Example: All are invited.
(सभी को निमंत्रित किया गया है।)- This sentence refers to a group of people, making it plural.
- None can also be singular or plural depending on the situation.
Example: None of the answers are correct.
(उत्तरों में से कोई भी सही नहीं है।) - Some can be singular or plural.
Example: Some of the water has evaporated.
(पानी का कुछ हिस्सा वाष्पित हो गया है।)
Example: Some of the students were late.
(कुछ छात्र देर से आए थे।)
Key Points to Remember
- Indefinite pronouns refer to people or things in a general, non-specific way.
- Some indefinite pronouns are always singular (e.g., someone, something, nobody), while others are always plural (e.g., few, many).
- Certain indefinite pronouns, like all, none, and some, can be singular or plural depending on the context.
- Indefinite pronouns help make sentences smoother when you don’t need to refer to a specific person or thing.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Distributive Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition:
A distributive pronoun is used to refer to people or things one at a time, rather than collectively. These pronouns emphasize individuals within a group. The most common distributive pronouns are each, either, and neither.
- Each refers to every individual member of a group separately.
- Either refers to one of two options.
- Neither refers to none of the two options.
In Hindi, distributive pronouns are often translated as “प्रत्येक,” “दोनों में से एक,” and “दोनों में से कोई नहीं.”
Distributive Pronouns in English
- Each: Refers to every single person or thing in a group, one by one.
- Either: Refers to one of two people or things.
- Neither: Refers to none of two people or things.
Examples with Hindi Translations
- Each (प्रत्येक)
- Each of the students has completed their work.
(प्रत्येक छात्र ने अपना काम पूरा कर लिया है।) - Each player on the team has a different role.
(टीम के प्रत्येक खिलाड़ी की एक अलग भूमिका है।)
- Each of the students has completed their work.
- Either (दोनों में से एक)
- You can choose either book.
(आप दोनों में से कोई भी किताब चुन सकते हैं।) - Either of the roads will take you to the city.
(दोनों में से कोई भी सड़क आपको शहर तक पहुंचा देगी।)
- You can choose either book.
- Neither (दोनों में से कोई नहीं)
- Neither of the answers is correct.
(दोनों में से कोई भी उत्तर सही नहीं है।) - Neither of the options appeals to me.
(दोनों में से कोई भी विकल्प मुझे पसंद नहीं आया।)
- Neither of the answers is correct.
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
Each
The distributive pronoun each refers to every individual member of a group separately. It emphasizes individual actions or characteristics.
- Each student must submit the assignment.
(प्रत्येक छात्र को असाइनमेंट जमा करना होगा।)- Here, “each” refers to every student individually.
- Each of the books is interesting.
(प्रत्येक पुस्तक दिलचस्प है।)- “Each” indicates that every single book is interesting on its own.
Either
The distributive pronoun either is used when referring to one of two choices or options. It indicates that only one of the two is considered.
- You can have either coffee or tea.
(आप कॉफी या चाय में से एक चुन सकते हैं।)- “Either” means only one of the two drinks can be chosen.
- Either option is acceptable.
(दोनों में से कोई भी विकल्प स्वीकार्य है।)- This sentence means one of the two options is fine, without specifying which.
Neither
The distributive pronoun neither is used to refer to none of the two choices or options. It expresses a negative sense, meaning that none of the options are suitable.
- Neither of them speaks French.
(दोनों में से कोई भी फ्रेंच नहीं बोलता है।)- Here, “neither” indicates that none of the two people can speak French.
- Neither movie is worth watching.
(दोनों में से कोई भी फिल्म देखने लायक नहीं है।)- “Neither” means that both movies are unsatisfactory.
Key Points to Remember
- Each is used when talking about individuals in a group, emphasizing them one by one.
Example: Each of the students passed the test.
(प्रत्येक छात्र ने परीक्षा उत्तीर्ण की।) - Either is used to refer to one of two options.
Example: Either of you can go.
(तुम दोनों में से कोई एक जा सकता है।) - Neither is used when none of the two options are acceptable.
Example: Neither of the answers is correct.
(दोनों में से कोई भी उत्तर सही नहीं है।)
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
Relative Pronouns: Definition and Examples
Definition:
A relative pronoun is a word that introduces a relative clause and connects it to the noun or pronoun it modifies. Relative pronouns provide more information about the noun or pronoun in the main clause. Common relative pronouns in English are who, whom, whose, which, and that.
In Hindi, relative pronouns are translated as “जो,” “जिसे,” “जिसका,” etc., and they are used to link clauses together and provide additional information about a person, thing, or possession.
Common Relative Pronouns
- Who: Refers to people and is used as the subject of a clause.
- Whom: Refers to people and is used as the object of a clause.
- Whose: Refers to possession.
- Which: Refers to things or animals.
- That: Refers to people, animals, or things and can be used in defining relative clauses.
Examples with Hindi Translations
- Who (जो, जिसने)
- The teacher who explained the lesson is very kind.
(वह शिक्षक जिसने पाठ समझाया, बहुत दयालु है।) - She is the girl who won the competition.
(वह लड़की है जिसने प्रतियोगिता जीती।)
- The teacher who explained the lesson is very kind.
- Whom (जिसे, जिसे)
- The person whom you called is my friend.
(जिस व्यक्ति को आपने बुलाया था, वह मेरा दोस्त है।) - He is the man whom I saw at the market.
(वह वह आदमी है जिसे मैंने बाजार में देखा था।)
- The person whom you called is my friend.
- Whose (जिसका, जिनका)
- This is the boy whose father is a doctor.
(यह वह लड़का है जिसका पिता डॉक्टर है।) - The woman whose car was stolen is very upset.
(वह महिला जिसकी कार चोरी हो गई थी, बहुत परेशान है।)
- This is the boy whose father is a doctor.
- Which (जो, जिसे)
- This is the book which I was talking about.
(यह वह किताब है जिसके बारे में मैं बात कर रहा था।) - The house, which was painted last year, looks beautiful.
(वह घर, जिसे पिछले साल रंगा गया था, बहुत सुंदर दिखता है।)
- This is the book which I was talking about.
- That (जो, वह)
- This is the movie that I liked the most.
(यह वह फिल्म है जो मुझे सबसे ज्यादा पसंद आई।) - The dog that barked last night is very friendly.
(वह कुत्ता जिसने कल रात भौंका, बहुत दोस्ताना है।)
- This is the movie that I liked the most.
Detailed Explanation with Hindi Translation
Who
The relative pronoun who is used to refer to people and functions as the subject of a relative clause. It provides more information about a person mentioned earlier in the sentence.
- The girl who is standing there is my sister.
(वह लड़की जो वहां खड़ी है, मेरी बहन है।)- Here, “who” refers to the girl and connects the clause providing more details about her.
Whom
The relative pronoun whom is used to refer to people and functions as the object of a relative clause. It often follows prepositions and helps in describing someone who is the object of the action.
- The person whom you met yesterday is my boss.
(वह व्यक्ति जिसे आपने कल मिला था, मेरा बॉस है।)- “Whom” is used here to indicate that the person is the object of the action (met).
Whose
The relative pronoun whose indicates possession. It is used to show that something belongs to someone.
- She is the girl whose brother is an engineer.
(वह लड़की है जिसका भाई इंजीनियर है।)- “Whose” shows that the brother belongs to the girl.
Which
The relative pronoun which is used for things or animals. It introduces extra information about a thing or animal mentioned earlier.
- The car which I bought last year is very fast.
(वह कार जिसे मैंने पिछले साल खरीदा था, बहुत तेज़ है।)- “Which” introduces the clause that provides more information about the car.
That
The relative pronoun that is used for people, animals, and things. It is commonly used in defining relative clauses, which provide essential information to identify the subject.
- The cake that she baked was delicious.
(वह केक जो उसने बेक किया था, स्वादिष्ट था।)- “That” connects the clause “that she baked” to describe the cake.
Key Points to Remember
- Who is used to refer to people and functions as the subject of the clause.
Example: The woman who is speaking is a doctor.
(वह महिला जो बोल रही है, एक डॉक्टर है।) - Whom is used to refer to people and functions as the object of the clause.
Example: The person whom I invited is my friend.
(वह व्यक्ति जिसे मैंने बुलाया, मेरा दोस्त है।) - Whose is used to indicate possession.
Example: The boy whose bike was stolen is sad.
(वह लड़का जिसकी साइकिल चोरी हो गई थी, उदास है।) - Which is used to refer to things or animals.
Example: The movie which I watched was excellent.
(वह फिल्म जिसे मैंने देखा, बेहतरीन थी।) - That is used for people, animals, and things and is often used in defining clauses.
Example: The book that I borrowed is interesting.
(वह किताब जो मैंने उधार ली थी, दिलचस्प है।)
Examples Summary
- Who (जो, जिसने)
- The man who called me is my boss.
(वह आदमी जिसने मुझे फोन किया, मेरा बॉस है।)
- The man who called me is my boss.
- Whom (जिसे)
- The girl whom you met is my friend.
(वह लड़की जिसे आपने मिला, मेरी दोस्त है।)
- The girl whom you met is my friend.
- Whose (जिसका, जिनका)
- The woman whose car was parked here is angry.
(वह महिला जिसकी कार यहां खड़ी थी, गुस्से में है।)
- The woman whose car was parked here is angry.
- Which (जो)
- The painting which was sold last week is very famous.
(वह पेंटिंग जो पिछले हफ्ते बेची गई थी, बहुत प्रसिद्ध है।)
- The painting which was sold last week is very famous.
- That (जो, वह)
- The phone that I bought is expensive.
(वह फोन जो मैंने खरीदा, महंगा है।)
- The phone that I bought is expensive.
Relative pronouns are essential for connecting ideas in sentences, making them more descriptive and informative. Proper usage of who, whom, whose, which, and that helps create clear and coherent sentences in both English and Hindi.
Pronouns and Their Kinds in English Grammar
English Grammar in Hindi
Present Continuous Tense Rules and Uses
Present Continuous Tense Rules in Hindi
Tenses Fill in the Blanks Exercise Set-10
Sentences of Past Perfect Tense in Hindi and English
600+ Fixed Preposition with Hindi Part-2
400 Phrasal Verbs with Hindi Part-1
Prepositions in English Grammar in Hindi
Until Uses and Examples in Hindi
Degrees of Comparison Exercises – Set-1